Laravel already includes features or configurations for dealing with various types of errors. In this tutorial, we will look at what errors are and how to handle them in Laravel. When we are working on an application project, if a code error or an error occurs, we obviously want the error to be visible.
So, by inspecting the error message, we can determine which section contains an error. As a result, we can easily find and fix these bugs.
However, once our application project is deployed and operational, it would be preferable if the error was not visible on the front end. because it is not a good user experience strategy
Laravel Errors and Logging
Well, laravel already provides this configuration. configuration to hide and show errors. the error configuration in laravel is in the .env file .
Look for the APP_DEBUG section, and set it to true or false. By default, the setting is true. so that the error can be seen.
.env
If our Laravel project is finished and ready to go online, it's a good idea to change the APP_DEBUG setting to false. so that the error is no longer visible to the user.
It's not that by hiding this laravel error we can no longer see the error in our application.
Yes, we can see it in the log file generated automatically by Laravel. It's in the storage/logs folder.
Laravel will create log files and fill them with errors or processes that occur. and separated by date. so that it is easier for us to analyze.
Let's make an example, yes, now change the APP_DEBUG setting to false . so the error is no longer visible. now we try to make an error. create a new route.
routes/web.php
We instruct the route that we created to access the index() method in the ExampleController.php controller . but the controller is NOT made. because we pretend we forgot to make the controller so it's an error. now run the project.
php artisan serve
and access address
localhost:8000/mikinote
Look at the results, which should show an error message. But since we set false on APP_DEBUG, the error is not visible. but replaced with an error page of 500.

Laravel error handling.
An error message should appear that the ExampleController controller and index() method do not exist or have not been created.
But since we set the APP_DEBUG to false, the invisible error is replaced with the 500 error page to hide the error.
Please, friends, open the storage/logs folder to see the error. view log files with today's date format.
 Laravel error and logging
Laravel error and loggingAs seen in the logs, there is a notification that the ExampleController controller does not exist.
Here's the error documentation and logging from Laravel.
Showing Laravel Error Message
To display an error message in Laravel, we can use the abort() method. and fill in the error number you want to use. For example, 404, 403,500, and others.
404 = Error because the page was not found
403 = Error due to access rights (forbidden).
500 = Error because there is an error in the server/code
and others.
The following is an example of displaying an error message in Laravel.
You can apply this method directly to the route or controller.
create an example route like the following.
routes/web.php
in this example route we will use the index() method on the ExampleController.php controller.
So we will send the name data entered in the url to the index() method in the ExampleController.php controller.
Because we don't have the controller yet, we now create a new controller with the name ExampleController.php.
app/Http/Controllers/ExampleController.php
Okay, in the index() method, we capture the name data entered in the url, then we check if the name is "mikinote", then we display a 403 error page, with the message "You do not have access because you are too lazy to code."
If the name is "sera," then we return the value of the name. If all conditions are not met, then we display a 404 error page.
As I explained earlier, to display an error page in Laravel, we can use the abort() method or function. and we fill in the error number that we want. For example, 404, 403, 500 and others.
The second parameter is only optional, meaning it may or may not be filled in. If we fill in the second parameter, then the error message displayed on the error page is the message we created.
Otherwise, the error message displayed is the default error message on the laravel error page. In the example above, I have demonstrated both the abort() and write() models.
We'll see the results. access localhost: 8000/mikinote/nothing.
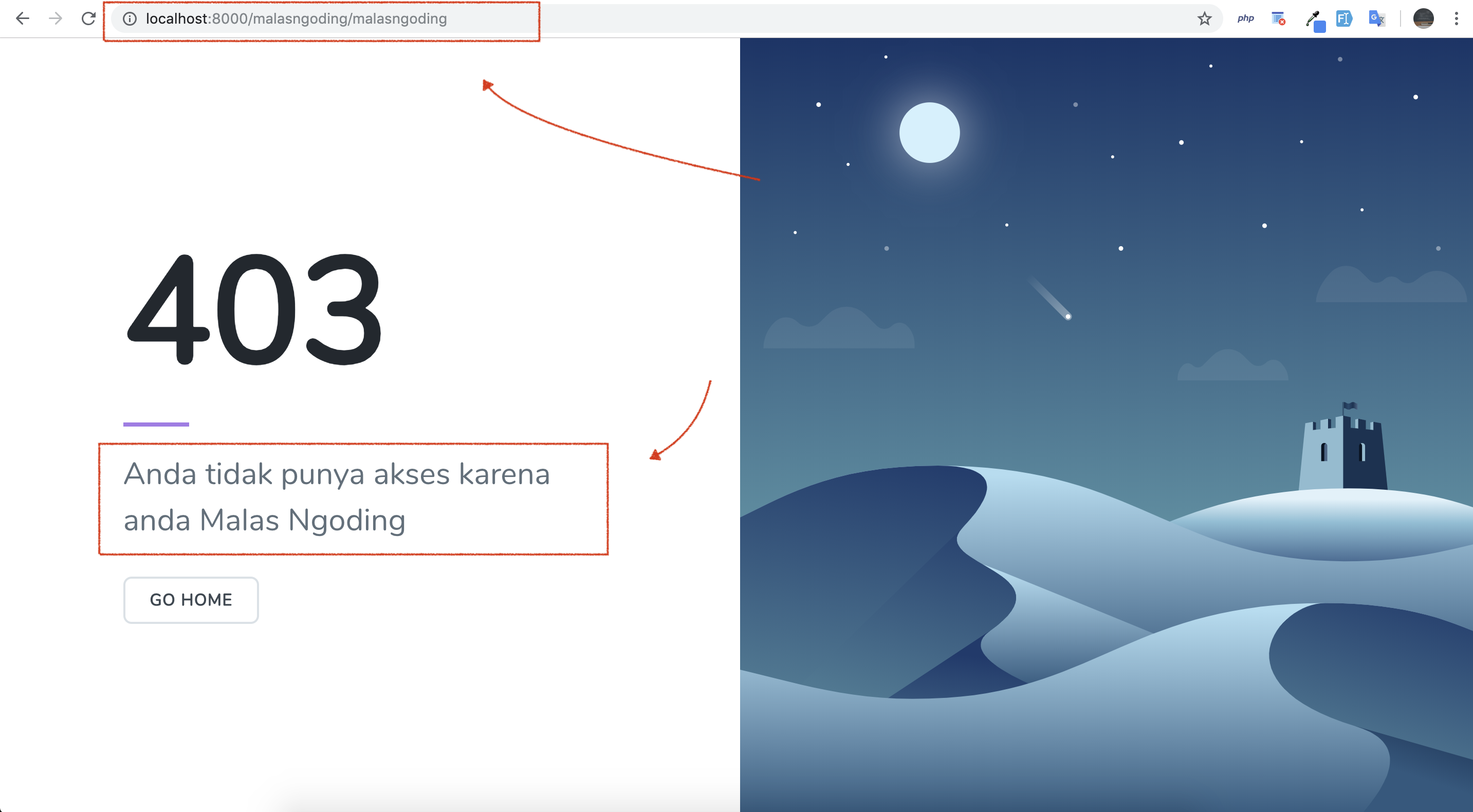
displaying laravel 403 forbidden page
Now try to access localhost:8000/mikinote/sera .

display laravel error page
As seen in the picture above, because what we input is "sera", then the value $name is displayed. and try if we can access localhost:8000/mikinote/drack.

showing laravel 404 page
Then a 404 error page will appear.
Changing the Laravel Error Appearance
We can also change the appearance of the laravel error page. how to type the following artisan command.
After typing the artisan command above, Laravel will create an errors folder in the views folder. In this errors folder, there are Laravel error page view files that you can directly change as you wish.

change laravel error page view


Post a Comment
Post a Comment